[Ingredients]
The main ingredient of this product is metformin hydrochloride.
Chemical name: 1,1-dimethylbiguanidine hydrochloride.
Chemical structural formula:
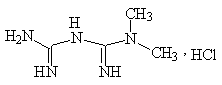
Molecular formula: C4H11N5 · HCl
Molecular weight: 165.63
[Character]
This product is a white to almost white circular film coated tablet. After removing the coating, it appears as a white to almost white circular tablet.
[Indications]
This product is preferred to be used for type 2 diabetes with simple diet control and physical exercise ineffective in controlling blood sugar.
For adults, this product can be used for monotherapy or in combination with sulfonylurea drugs or insulin.
For children and adolescents aged 10 and above, this product can be used for monotherapy or in combination with insulin therapy.
[Specification] 0.25g.
[Usage and dosage]
In order to reduce the occurrence of gastrointestinal complications and to use the minimum dose of medication to control the patient's blood sugar, it should be taken from a small dose and gradually increased.
At the beginning of treatment and during the adjustment of dose (see the recommended medication plan), the measurement of fasting blood glucose can be used to determine the treatment response of the product and determine the minimum effective dose of the patient. Afterwards, glycated hemoglobin should be measured every three months. Whether used alone or in combination, the goal of treatment is to use the lowest effective dose to reduce the fasting blood glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin levels to normal or near normal levels.
Recommended medication plan
Adults with normal renal function (eGFR ≥ 90mL/min/1.73m2)
Single drug therapy and combination therapy with sulfonylurea drugs
Oral administration, starting at 0.25g per dose for adults and children, 2-3 times a day. Gradually increase the dosage after 10-15 days based on the therapeutic effect, with a maximum recommended dose of 2g per day. Taking with meals can reduce gastrointestinal reactions.
Combined use with sulfonylurea drugs
If patients who have not responded after taking the maximum recommended dose of this product for several weeks should consider gradually adding sulfonylurea oral hypoglycemic drugs while maintaining the maximum dose treatment, unless the patient already has primary or secondary failure to sulfonylurea drugs. Currently, there are only clinical and pharmacokinetic data on the interaction between metformin and glibenclae (glibenclae).
Combining this product with sulfonylurea drugs can achieve satisfactory blood sugar control by adjusting the dosage of both drugs. The risk of hypoglycemia caused by sulfonylurea drugs continues to exist or even increases when treated with this product, and appropriate prevention should be taken.
If the patient cannot satisfactorily control their blood sugar after 1 to 3 months of treatment with the maximum dose of this product combined with the maximum dose of oral sulfonylurea drugs, consideration should be given to changing the treatment method, including the combination of this product with insulin therapy or insulin therapy alone.
Combined use with insulin
The dosage of insulin can be maintained when starting to use this product. The initial dose of this product should be 500 milligrams per day for patients undergoing insulin treatment. If the patient's response is not sufficient, add 0.5g after 1 week, and then add 0.5g every week until satisfactory blood sugar control is achieved. The recommended maximum daily dose is 2g. When the fasting blood glucose of patients who use this product in combination with insulin drops below 120mg/dL, it is recommended to reduce the insulin dosage by 10% to 25%. Individualized adjustments or medical advice should be continued based on the response to reduced blood sugar.
Dose adjustment in patients with impaired renal function
No dose adjustment is required for eGFR ≥ 60mL/min/1.73m2, eGFR 45-59mL/min/1.73m2 is reduced, and eGFR<45mL/min/1.73m2 is disabled.
[Adverse reactions]
According to foreign literature reports:
At the initial stage of treatment, the most common adverse reactions are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and loss of appetite, which most patients can usually alleviate on their own. The following adverse reactions may occur when taking metformin.
The frequency of adverse reactions is defined as follows: very common (≥ 10%); Common (1%~10%, including 1%), occasional (0.1%~1%, including 0.1%), rare (0.01%~0.1%, including 0.01%), very rare (<0.01%). In each frequency group, adverse reactions are arranged in descending order of severity.
Metabolic and nutritional disorders:
Very rare:
? Lactic acidosis (see Precautions)
? Long term use of metformin may reduce the absorption of vitamin B12. If the patient experiences megaloblastic anemia, this reason should be considered.
Neurological abnormalities:
Common:
? Taste disorders
Gastrointestinal abnormalities:
Very common:
? Gastrointestinal abnormalities such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and loss of appetite. Most of these adverse reactions occur at the beginning of treatment, and most patients can usually alleviate them on their own. Slowly increasing the dose can improve gastrointestinal tolerance.
Abnormal liver and gallbladder function:
Very rare:
? Reports of individual cases with abnormal liver function tests or hepatitis returning to normal after discontinuing metformin administration.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue abnormalities:
Very rare:
? Skin reactions, such as erythema, itching, and urticaria.
Other possible adverse reactions include: bloating, fatigue, indigestion, abdominal discomfort and headache, abnormal bowel movements, constipation, bloating, hypoglycemia, muscle pain, dizziness, dizziness, abnormal nails, rash, increased sweating, chest discomfort, chills, flu symptoms, hot flashes, palpitations, weight loss, etc.
children
In published data, post market data, and a one-year clinical controlled study conducted in a limited number of children aged 10-16, adverse events and their severity were similar to those in adults.
[Taboos]
? Severe renal failure (eGFR<45mL/min/1.73m2);
? Acute conditions that may affect renal function, such as dehydration, severe infection, shock;
? Diseases that can cause tissue hypoxia (especially exacerbation of acute or onic diseases), such as decompensated heart failure, respiratory failure, recent myocardial infarction, and shock;
? Severe infections and injuries, major surgical procedures, clinical symptoms such as hypotension and hypoxia;
? Known allergies to metformin hydrochloride and any components in this product;
? Any acute metabolic acidosis, including lactic acidosis, diabetes ketoacidosis;
? The prodromal stage of Diabetic coma;
? Liver dysfunction, acute alcoholism, alcoholism;
? Individuals with uncorrected vitamin B12 and folic acid deficiencies.




各省份負(fù)責(zé)人聯(lián)系方式